2021.03.29 - [분류 전체보기] - 작업일정관리 사용자 설명서 (한국어판)
작업일정관리 사용자 설명서 (한국어판)
이 앱은 작은 정비업소등에서 사용할 수 있도록 개발된 앱입니다. 1. 이앱은 5가지 정도의 공정을 가지고 있는 정비업소에서 각 공정별로 입고되는 수리대상 품목(이하 수리차량이라 명칭)을 입
billcorea.tistory.com
This app is an app developed to be used in small maintenance shops.

1 This app supports the management of items subject to repair (hereinafter referred to as repair vehicles) that are worn by each process at a maintenance business that has about 5 processes, and manages them according to classifications such as painting, lower part, sheet metal, and inspection. It is an app to do.
2. Since the data is based on the Firebase Realtime Database, you can share real-time work status.
3. The user can use it for a certain period of time free of charge to determine whether or not to apply the business, and if he/she wants to continue using it, he/she can maintain the use through a monthly payment. (The administrator manages the backup with regular payment income if the data needs to be backed up.)
4. In this app, user management is based on the Google account email, but the user's email account is used only for user verification, and it is not allowed to be provided to the outside. (When registering a user, you can use an alias for the user name.)
5. The e-mail account used for initial registration is used as the account of the data manager, so please enter it carefully. If you delete the app later, if you re-register the user e-mail account, the existing data may be lost, so remember the administrator e-mail account well. Must be. (If necessary, upon request, we can inform you after confirmation.)
As shown in the screen above, if you enter the administrator's e-mail account and the user's company name during initial execution, it will be displayed on the screen.
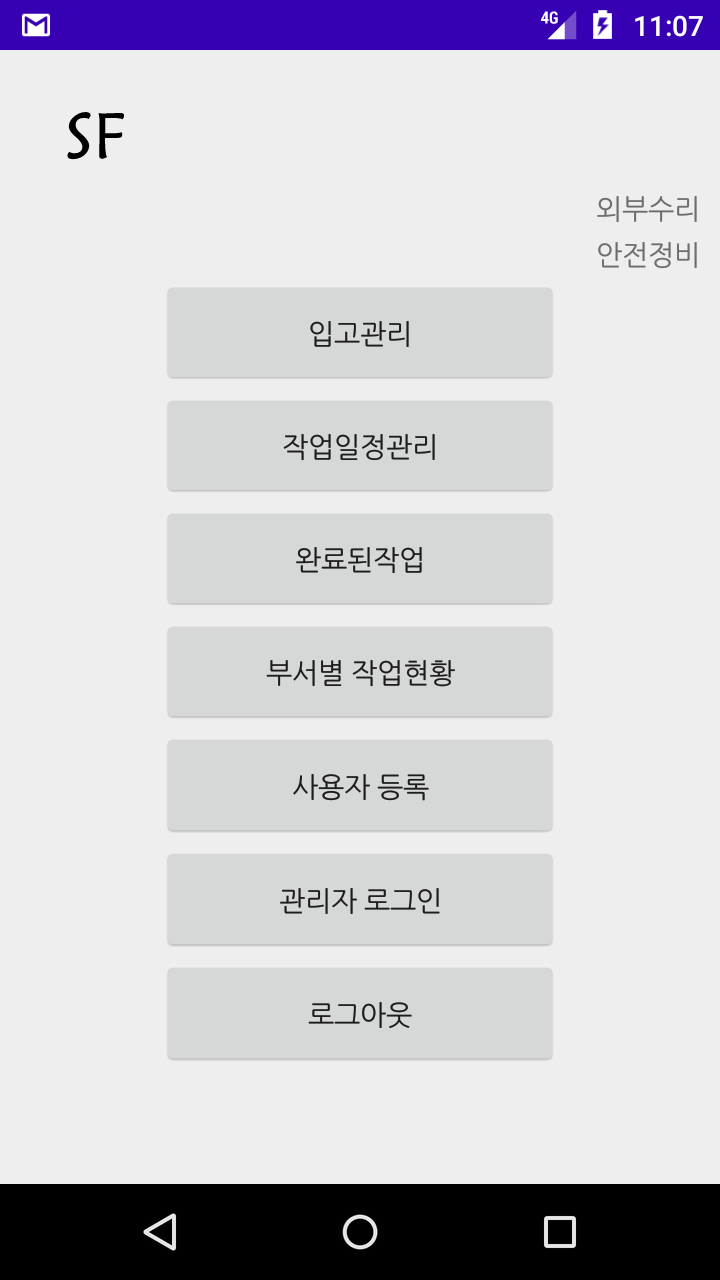
The basic menu composition of this app is as follows.
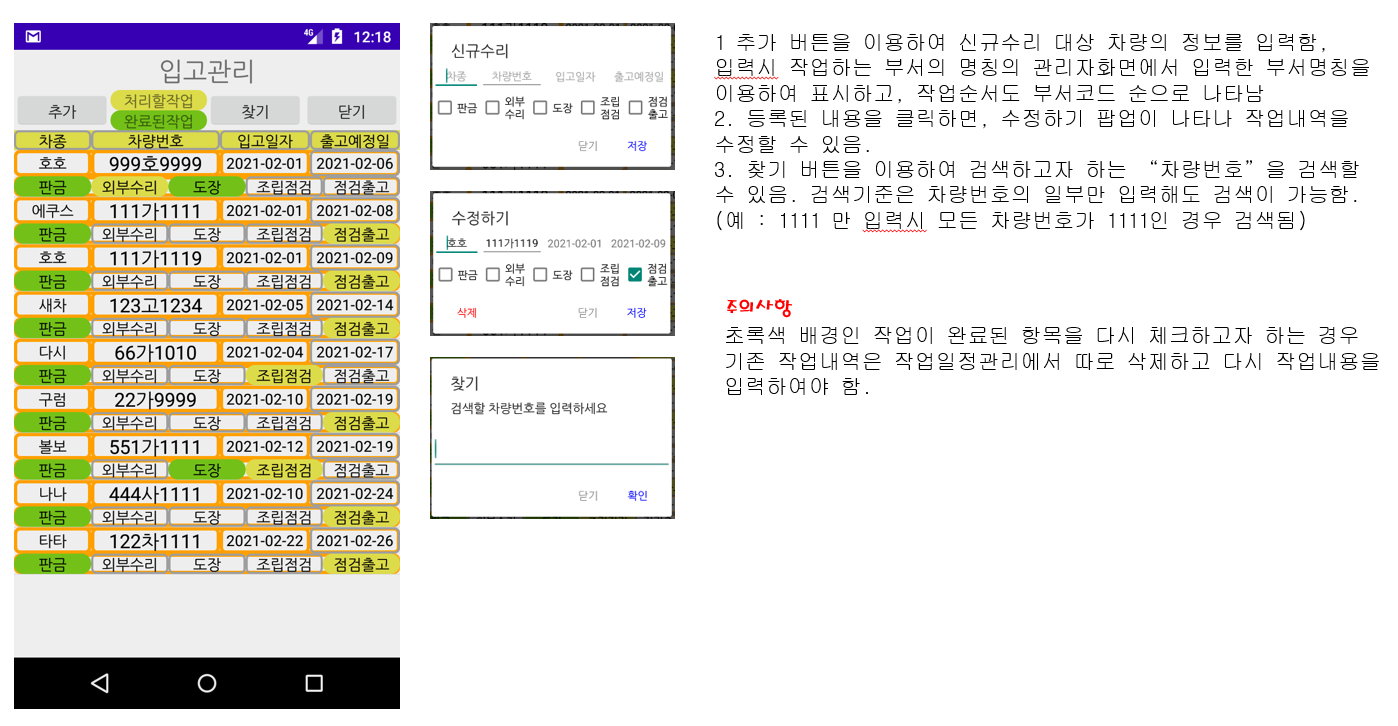
1. Receipt management: New vehicle registration screen
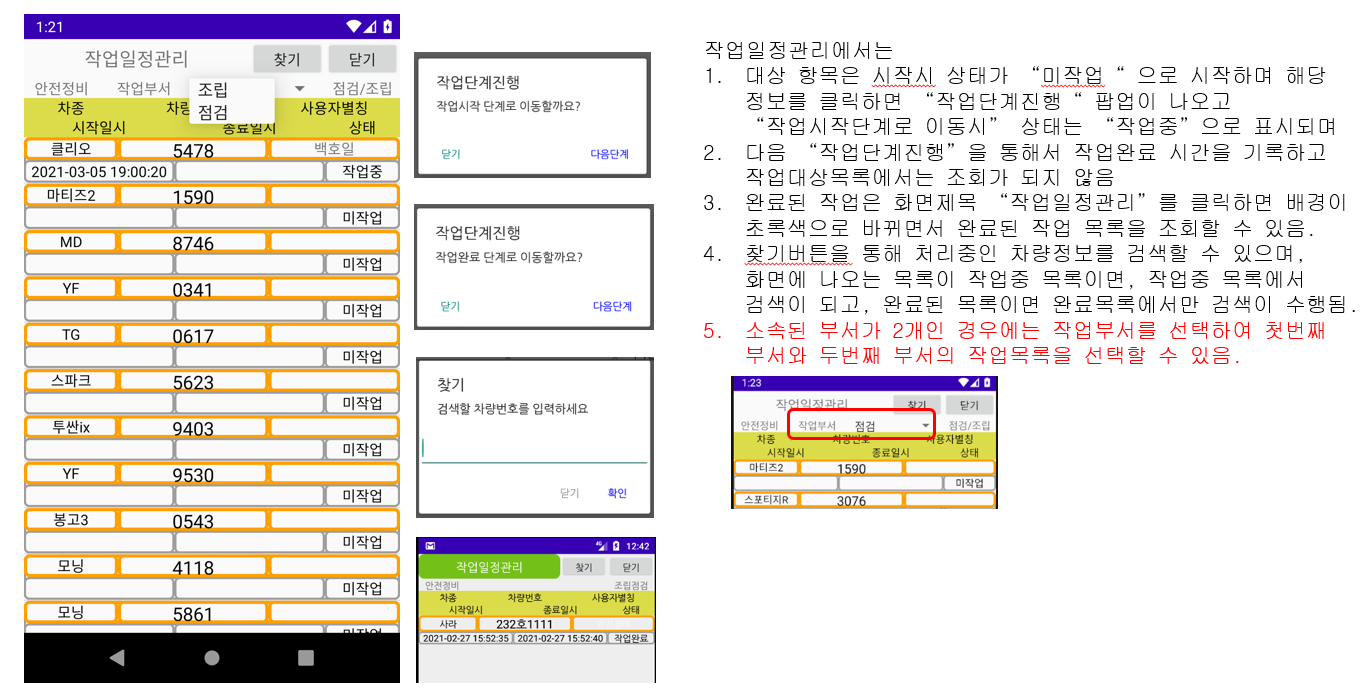
2. Work schedule management: Search the list of work targets by department and register the progress of work steps
3.Completed work: Search for completed targets from the work target list registered in warehousing management
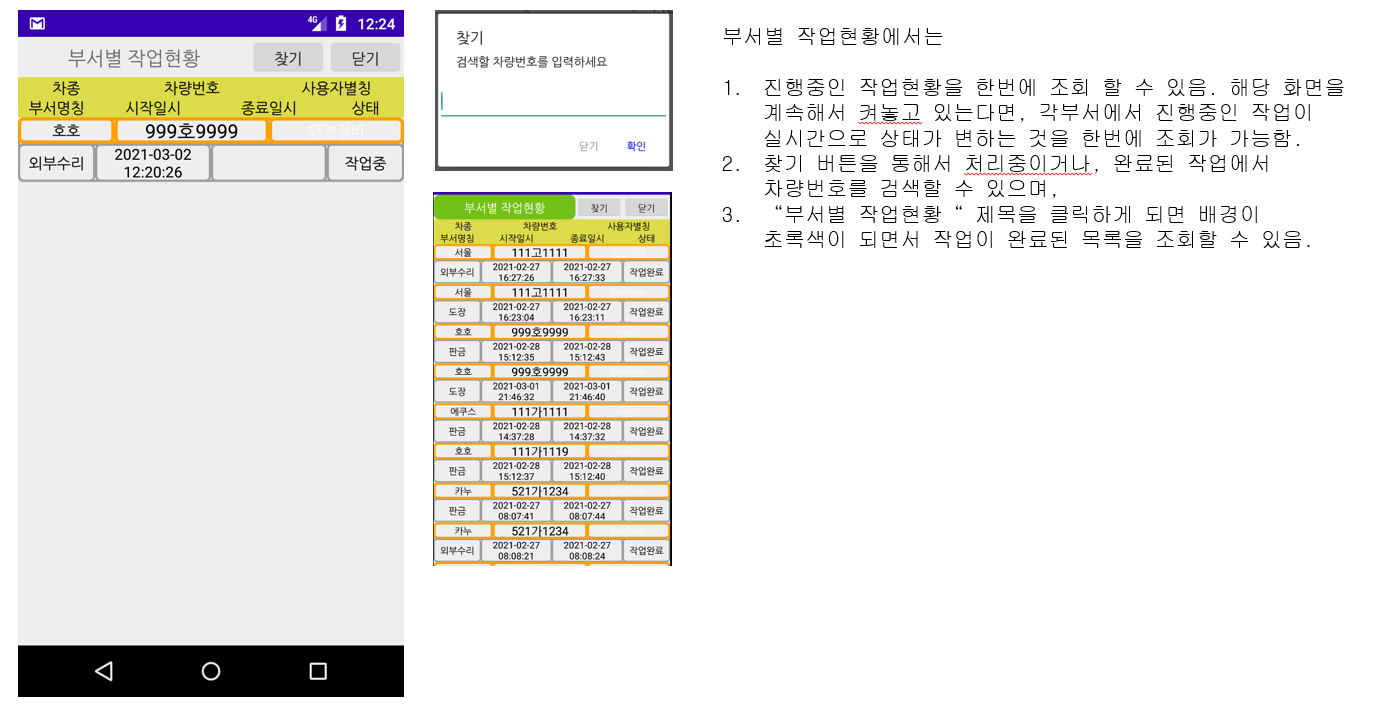
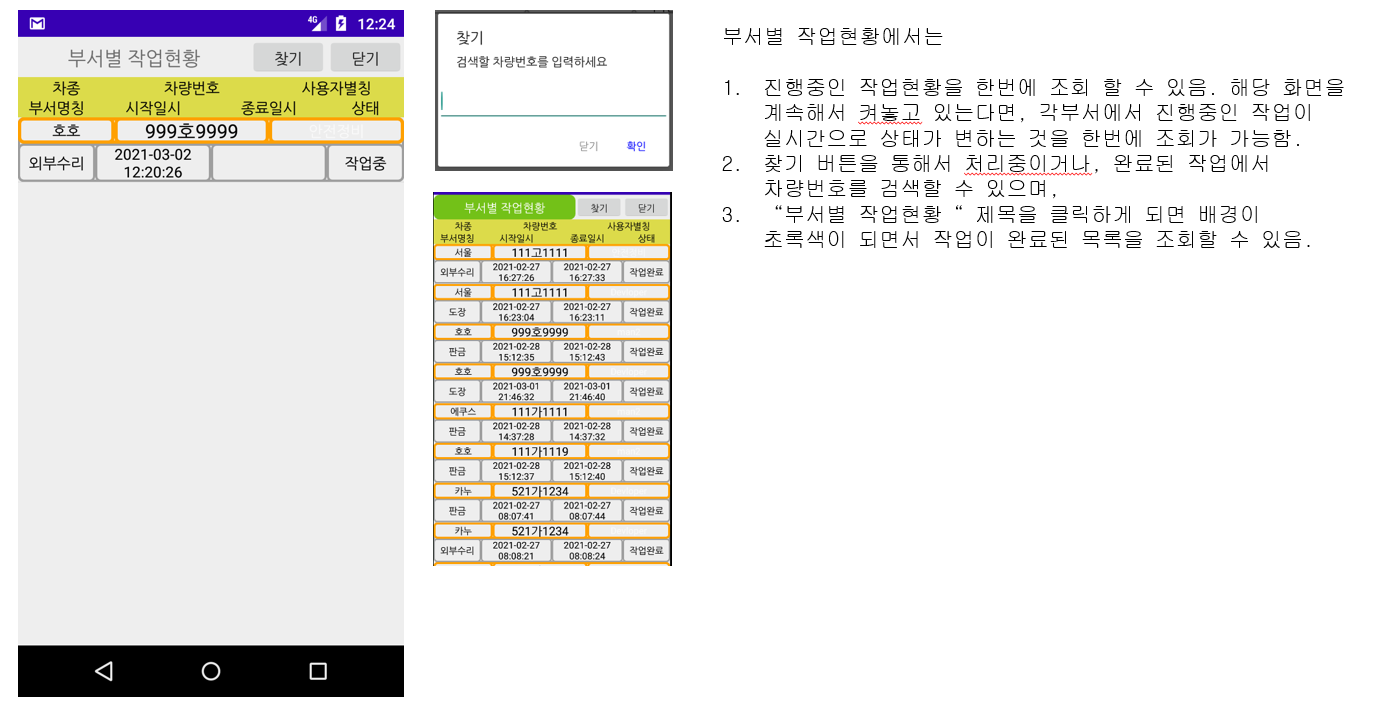
4. Job status by department: Inquiry of job status by department and list of completed jobs by department
5. User registration: Approval processing for users logged in with Google account and change of the user's department
6. Administrator login: Administrators can only use the account designated by default, and manage department codes and names.
7. Logout: Log out of this app and close the app
After login is completed using your Google account,
As shown in the following figure
If you select Administrator Login on the menu screen,

1. A Google login button appears, and login starts with the Google account you are using.
2. From the next time, you can select a registered account.
3. Only when logged in as an administrator
* Yellow background appears in email and user alias
* Save button is activated (If you are not an administrator, the save button is disabled)
4. You can add the department code by clicking the Add button, and the order of registration here
Since the work list is organized to match with, the department code
Must be registered by granting (Code value is not important, but if possible
It is given so that the order can be sorted using numbers)
5. When modifying the department code, click the column with the corresponding code to modify the department.
The screen appears.
After the user registration screen is switched through Google login,

1. User alias can be entered and saved, and departments can be selected, and the department name entered from the department name appears on the administrator screen.
2. You can choose to save or delete. (If you delete it, you will be logged out, so you need to log in again to save the user information)
3. Up to 2 department codes can be selected, and the second department must be blank if not selected.
4. When a user is saved, it is displayed on a gray background as shown in the figure below. In this case, the administrator must click the user on the screen and approve it to process the work.
5. In the case of an approved user, the approval can be canceled by selecting as shown in the left figure. Upon cancellation of approval, it should be checked whether the background is gray.
The order of business processing is
1. Registration of new vehicle information in stock management management

2. Work schedule management manages the work schedule for each department using the department code information of the logged-in user for each department.
(If you click a work target in the list, it proceeds to the next step, and the completed work disappears from the list)

3. In the completed work, depending on the number of repair parts selected at the time of initial registration on the warehousing management screen, when the work is completed, it disappears from warehousing management and information of the vehicle is displayed only in the completed work.

4. The work status of each department can be checked in real time when each department starts work.
If you are curious or need improvement, please let us know by e-mail and we will improve it.
Thank You !!!